Observer Selection
Epochs and Selection Timeline
The ar.io network operates on 24-hour epochs, during which the observer selection and evaluation process takes place. At the start of each epoch:
- 50 observers are selected to monitor the network
- 2 prescribed ArNS names are chosen for all observers to test
- 8 additional names are selected by each observer individually
- Gateway subset is selected for chunk/offset validation based on sampling rate
This creates a consistent evaluation framework where all observers test the same baseline names while having flexibility to choose additional targets for comprehensive network monitoring, plus advanced data integrity verification.
Selection Process
Up to fifty (50) gateways are selected as observers per epoch using a sophisticated weighted random selection system. The selection uses hashchain entropy from previous ar.io contract state messages to ensure unpredictable and tamper-resistant selection.
The hashchain-based entropy provides cryptographic randomness for selecting:
- Observer Gateways: The 50 gateways chosen to perform observations
- Prescribed ArNS Names: The 2 common names all observers must evaluate
This approach prevents manipulation while maintaining weighted probabilities based on gateway performance and commitment.
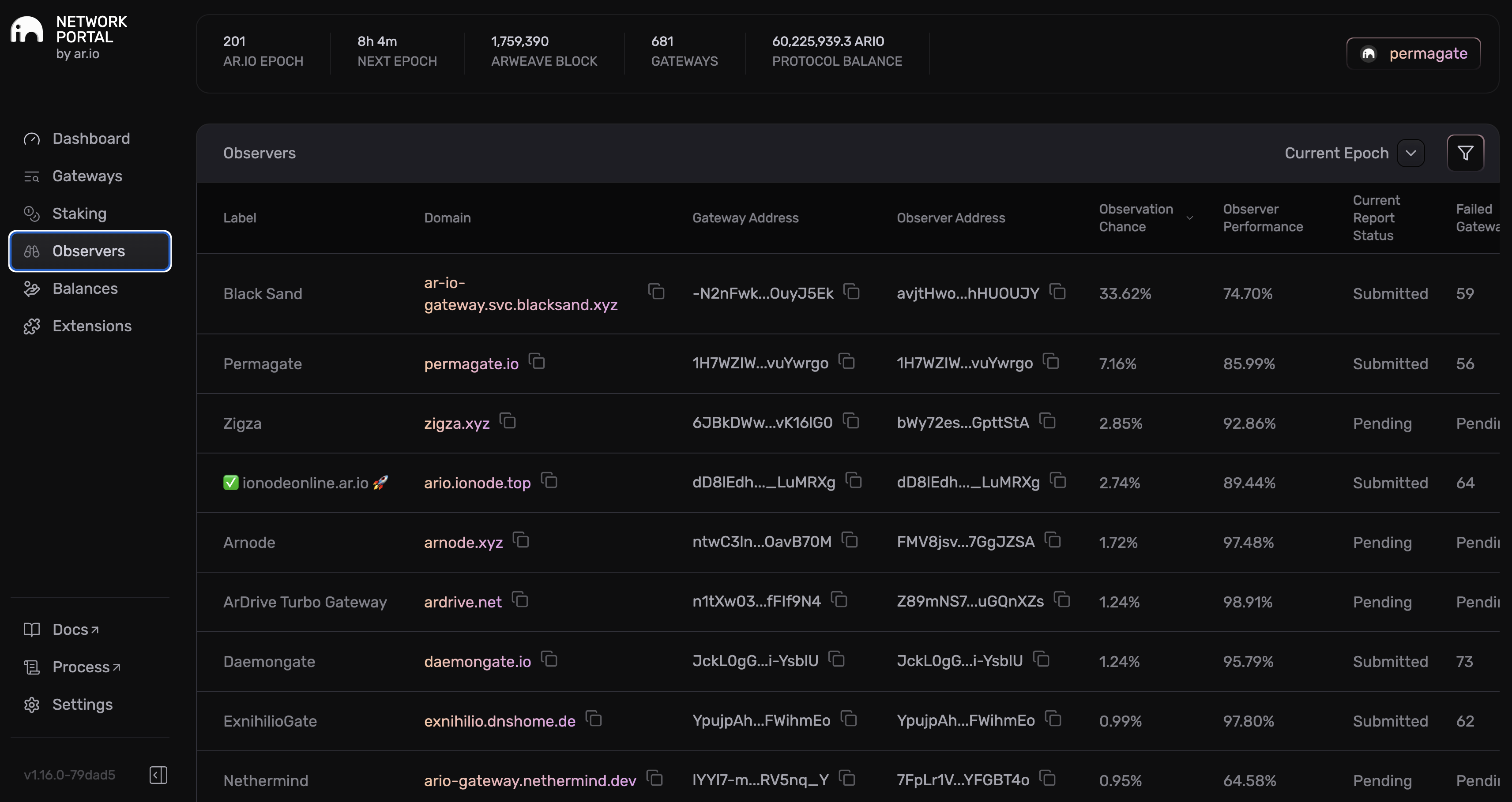
shows the current epoch prescribed observers and arns names, as well as their submission status
Weighted Selection Criteria
Observer selection is based on normalized composite weights that combine multiple performance and commitment factors. These weights determine each gateway's probability of being selected as an observer for the epoch.
The selection considers four key factors that are multiplied together to create a composite weight (CW):
- Stake Weight (SW): Financial commitment to the network
- Tenure Weight (TW): Length of network participation
- Gateway Performance Ratio Weight (GPRW): Historical gateway performance
- Observer Performance Ratio Weight (OPRW): Historical observer performance
These weights are then normalized across all eligible gateways to create selection probabilities. For detailed weight calculations and formulas, see Performance Evaluation.
Hashchain Random Selection
The selection process uses hashchain entropy from previous ar.io contract state messages to achieve cryptographically secure randomness:
How Hashchain Selection Works
- Entropy Source: Random numbers are generated from the hashchain of previous contract state messages
- Weighted Mapping: Each random number maps to normalized weight ranges of eligible gateways
- Observer Selection: The gateway whose weight range contains each random number is selected
- Prescribed Names: The same entropy selects 2 ArNS names that all observers must test
This creates tamper-resistant selection where higher-weighted gateways have proportionally better chances of selection, while maintaining true randomness that cannot be predicted or manipulated.
Chunk/Offset Sampling
In addition to observer selection, the protocol includes a separate sampling process for chunk/offset validation:
Gateway Selection for Chunk Validation
- Deterministic Selection: Uses PRNG seeded with observation entropy to select gateway subset
- Sampling Rate: Configurable percentage of gateways tested per observation (default: 1%)
- Minimum Guarantee: At least 1 gateway is always selected for testing
- Offset Selection: Random offsets within the stable weave range are chosen for each selected gateway
Initial Implementation: During the initial rollout phase, only a very small portion of gateways will be checked for chunk/offset validation, and the current validation criteria are extremely lenient to ensure smooth network operation.
Validation Process
- Chunk Retrieval: Observers request chunk data using
GET /chunk/{offset} - Merkle Proof Verification: Cryptographic validation ensures data integrity
- Early Stopping: Tests stop immediately upon first successful validation
- Performance Optimization: Uses LRU caching for efficient transaction lookup
Fairness and Meritocracy
This system ensures:
- Meritocratic Selection: Higher-performing gateways have better selection odds
- Fair Opportunity: All gateways maintain non-zero selection probability
- Tamper Resistance: Hashchain entropy prevents manipulation
- Consistent Standards: Prescribed names create common evaluation baseline
The selection is saved in the contract state at epoch start to ensure that activities during the epoch do not affect selection or reward distribution.
Next Steps
Ready to understand how performance is evaluated? Learn about Performance Evaluation to see how gateways are scored, or explore Reward Distribution to understand how rewards are calculated and distributed.
How is this guide?
Observation & Incentive Protocol
The Observation and Incentive Protocol is designed to maintain and enhance the operational integrity of gateways on the Ar.io Network through a combination of incentivizing gateways for good performance and tasking those gateways to fulfill the role of observers
Reporting
Learn about observer responsibilities for submitting reports to Arweave and the ar.io Smart Contract